Fouling
What is fouling?
Fouling is the attachment of contamination to the heat-transfer surface, which reduces the heat-transfer coefficiency. This leads to an increase in pressure-drop and higher energy consumption. In the worst cases, heavy contamination can damage the heat exchanger and even lead to failure.
Fouling can often be eliminated if it is discussed during the design phase. The correct mitigation of fouling begins with understanding the fouling mechanisms that can occur, which are typically divided into six main groups:
- particulate fouling
- crystallisation
- biological fouling
- chemical reactions
- solidification
- corrosion

Mitigation
The best way to mitigate fouling is good heat-exchanger design. Our experience of fouling problems and knowledge of heat-exchanger design make it possible to avoid fouling without the need for cleaning.
Vahterus can offer several plate corrugation angles and differing plate gaps, which can help prevent possible clogging from contaminants.
However, the most important thing is to understand how the flow between the plates can be processed in order to prevent any fouling material from attaching to the heat-transfer surfaces. High velocity near the heat-transfer surface is not only good for heat transfer, but also to mitigate fouling, since it creates high shear stress. Shear stress is the result of pressure drop and heat-exchanger geometry.
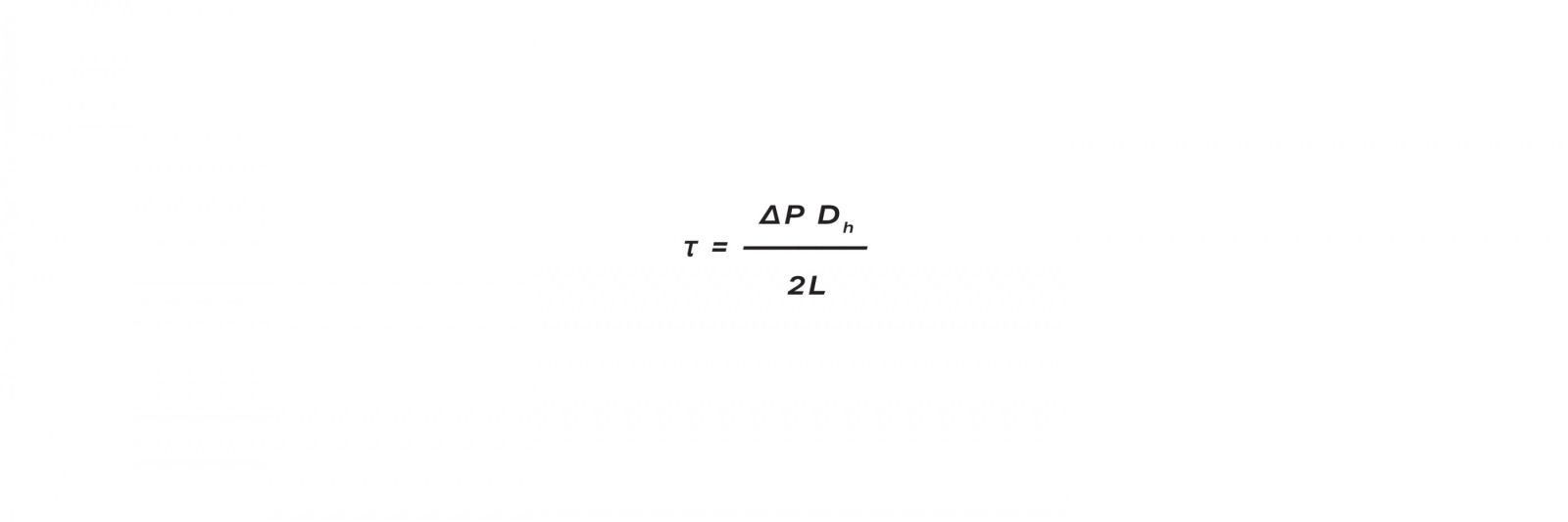
The shorter the path through the heat exchanger, the higher the shear stress will be. This is why long Shell & Tube type heat exchangers have far less shear stress, thus are more prone to fouling than Plate & Shell Heat Exchangers.
What if cleaning is needed?
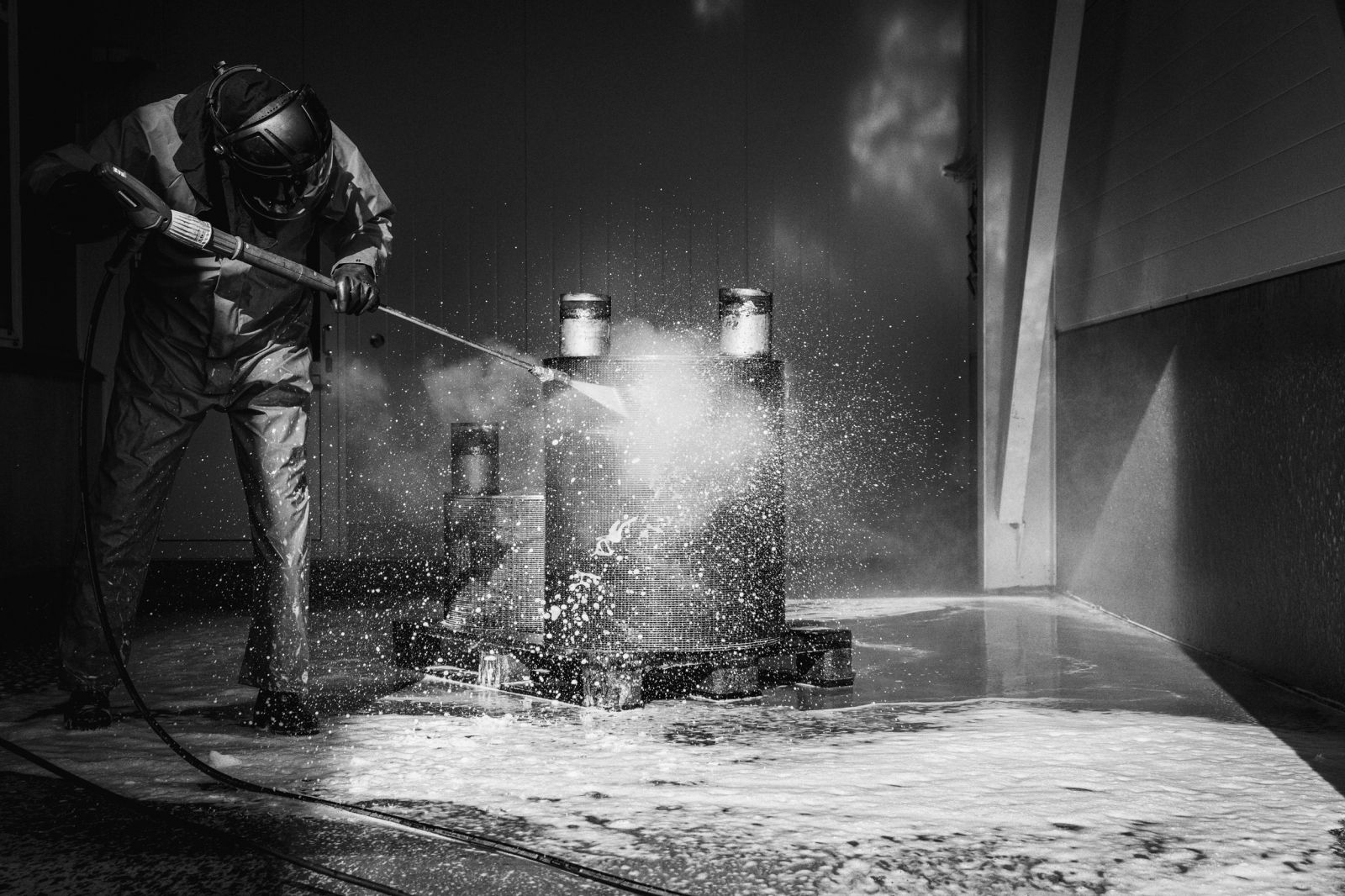
Sometimes, even good heat-exchanger design cannot prevent fouling. In these cases, an effective and economical cleaning process is required.
The most suitable cleaning method is selected once the contamination and type of heat exchanger have been identified.
Vahterus Service offers a number of Cleaning Methods and Performance Checks of existing heat exchangers. Cleaning and tests can be done either in-house at the Vahterus facility or on site.
Watch video above for Vahterus Plate & Shell Heat Exchanger Cleaning Methods
